Breast Reconstruction Surgery in Málaga
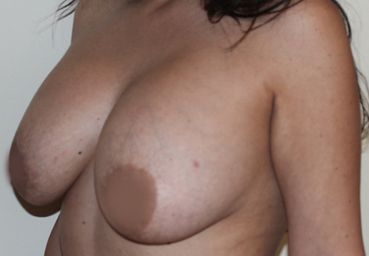
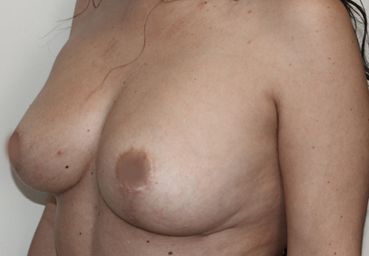
After the removal of the breast due to oncological reasons or after experiencing an accident, a breast reconstruction process is performed. This can be done in three different ways: skin expansion of the mastectomized chest, flaps that provide tissue to the breast being reconstructed, or the transfer of the patient’s own fat through lipofilling or lipotransfer. All these procedures can be combined. The choice of one or another method will depend on the characteristics of the skin, the mastectomized chest, and the patient’s preferences.
Dr. Javier Collado, after a thorough examination, will explain in detail which alternative best suits your characteristics. The ultimate goal will always be to achieve the highest possible symmetry between both breasts, so in many cases, an intervention on the healthy breast will be necessary, either to enhance, lift, or reduce it.

Breast reconstruction specialists.
Here are some health benefits for patients who opt for breast reconstruction:
- Excellent results, regardless of the patient's age.
- Enhancement of breast aesthetics.
- Improved patient self-esteem.
- Scars are barely noticeable to the patient.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this procedure, a non-permanent implant is placed in the area where the mammary gland used to be. After the wounds have healed, expansion or filling begins, usually done in 3 or 4 sessions. Once the desired volume is reached, the implant is replaced with a permanent one. To carry out this type of reconstruction, quality skin tissue is essential, preferably non-irradiated, to serve as a foundation for the expander; otherwise, there’s a risk of failure.
There are three areas from which healthy tissue can be harvested for breast reconstruction: the back, abdomen, or buttocks.
This is also known as the latissimus dorsi flap, which involves moving this muscle from the back to the chest. It usually needs to be paired with an expander, as this method provides quality skin for reconstruction. However, it often doesn’t provide sufficient volume, so a breast implant may also be needed.
Known as the DIEP flap, this procedure transplants excess fat and skin from the lower abdomen to the breast being reconstructed. It’s the preferred technique when abdominal tissue is available, but it requires an experienced surgeon, as it involves suturing blood vessels of 1 to 2 mm thickness under microscopic vision. The result is an aesthetic improvement of the abdomen, similar to an abdominoplasty, and a reconstructed breast with sufficient volume that may not require an implant.
This would be the second-choice technique, only if the DIEP flap is unavailable.